Types of Cheques







Types of Cheques
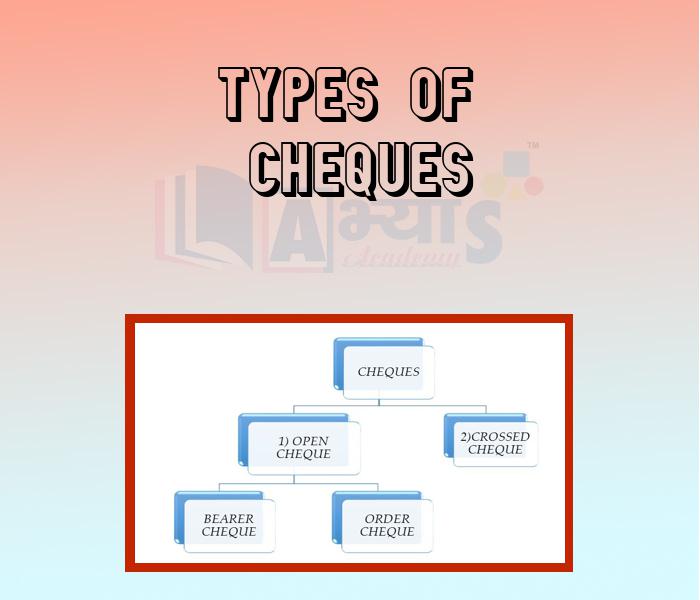
Types of Cheques :
Types of Crossing:
(a) General Crossing : In a general crossing, simply two parallel transerve lines, with or without the words the words not negotiable in between, may be drawn. Such a cheque is crossed generally. The effect of general crossing is that the payment of the cheque will not be made at the counter; it can be collected only through a banker.
(b) Special Crossing: In a special crossing, the name of a banker with or without the words not negotiable is written on the cheque. Such a cheque is crossed specially to that banker .The effect to special crossing is that the paying banker will transfer the amount of the cheque only through the bank named in the cheque.It should be noted that two transverse parallel lines are necessary for a general crossing, whereas for a special crossing, no such lines are necessary.
(c) Restrictive Crossing: This type of crossing has been recognised by usage and custom the trade. In a restrictive crossing, the words 'Account Payee' or 'Account Payee Only are added to the general or special crossing The effect of restrictive crossing is that the payment of the cheque will be made by the bank to the collecting banker only for the account payee named. If the collecting banker collects the amount for any other person, he will be liable for wrongful conversion of funds.
(d) Not Negotiable Crossing: A cheque crossed generally or specially, bearing in either the words 'not negotiable' shall not be able to give a better title to the holder than that of the transferor. The effect of a not negotiable crossing is that the cheque can be transferred but the transferred will not acquire a better title to the cheque. Thus, a cheque is deprived of its essential features of negotiability. The object of "not negotiable" crossing is to protect the drawer against loss or theft in the course of transit.
5. Ante-Dated Cheque: If a cheque bears a date earlier than the date on which it is presented to the bank, it is called as "anti-dated cheque". Such a cheque is valid upto three months from the date of the cheque.
6. Post-Dated Cheque: If a cheque bears a date which is yet to come (future date), then it is known as post dated cheque. A post dated cheque cannot be honoured earlier than the date on the cheque
7. Stale Cheque: If a cheque is presented for payment after three months from the date of the cheque, it is called stale cheque. A stale cheque is not honoured by the bank.
Account Payee Cheques can be paid _________________ | |||
| Right Option : C | |||
| View Explanation | |||
Students / Parents Reviews [10]
I have spent a wonderful time in Abhyas academy. It has made my reasoning more apt, English more stronger and Maths an interesting subject for me. It has given me a habbit of self studying

Yatharthi Sharma
10thMy experience with Abhyas is very good. I have learnt many things here like vedic maths and reasoning also. Teachers here first take our doubts and then there are assignments to verify our weak points.

Shivam Rana
7thIt was good as the experience because as we had come here we had been improved in a such envirnment created here.Extra is taught which is beneficial for future.

Eshan Arora
8thIt was a good experience with Abhyas Academy. I even faced problems in starting but slowly and steadily overcomed. Especially reasoning classes helped me a lot.

Cheshta
10thIt has a great methodology. Students here can get analysis to their test quickly.We can learn easily through PPTs and the testing methods are good. We know that where we have to practice

Barkha Arora
10thA marvelous experience with Abhyas. I am glad to share that my ward has achieved more than enough at the Ambala ABHYAS centre. Years have passed on and more and more he has gained. May the centre flourish and develop day by day by the grace of God.

Archit Segal
7thMy experience was very good with Abhyas academy. I am studying here from 6th class and I am satisfied by its results in my life. I improved a lot here ahead of school syllabus.

Ayan Ghosh
8thAbhyas is a complete education Institute. Here extreme care is taken by teacher with the help of regular exam. Extra classes also conducted by the institute, if the student is weak.

Om Umang
10thMy experience with Abhyas academy is very good. I did not think that my every subject coming here will be so strong. The main thing is that the online tests had made me learn here more things.

Hiya Gupta
8thAbout Abhyas metholodology the teachers are very nice and hardworking toward students.The Centre Head Mrs Anu Sethi is also a brilliant teacher.Abhyas has taught me how to overcome problems and has always taken my doubts and suppoeted me.
